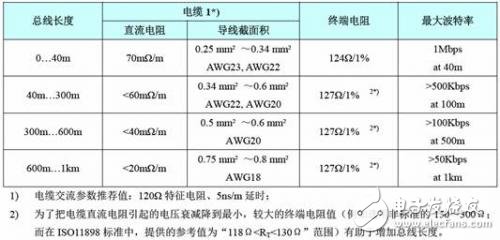
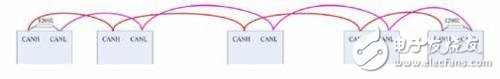
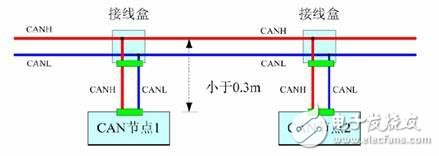
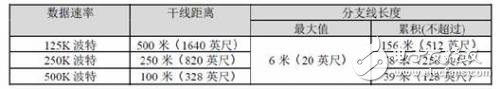
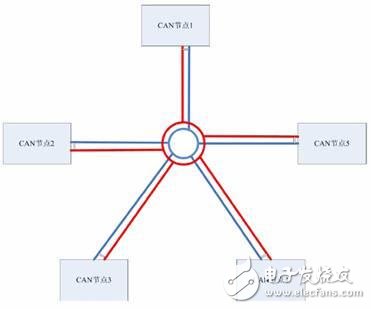
The so-called sharpening of the knife does not miss the chopping power, reasonable bus layout and wiring is equal to half of the success, then how to select the wire when the bus wiring? How to choose the wiring topology? First, wire selection 1, wire type Twisted pair cables must be used for CAN bus wiring, and twisted pairs with characteristic impedance of about 120Ω are required. In the case of long communication distance or poor electromagnetic environment, it is better to use shielded twisted pair cable, which can effectively suppress electromagnetic interference and ensure Reliable communication. 2, line length and DC resistance When the customer's communication distance is long, the line loss has to be considered. If the cable used is too thin, the DC resistance of the wire is too large. Then the signal sent at the beginning of the bus will abruptly attenuate when it reaches the end of the node after a long journey, eventually leading to communication failure. Then what is the relationship between the line length and the cross-sectional area of ​​the transmission line, and the line length and the communication baud rate? We summarize as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Transmission line related parameter recommended value Second, the wiring topology 1, "hand in hand" connection In the linear topology, due to the existence of a certain length of the branch and the accumulation of the length of the branch, the impedance on the bus is discontinuous, which in turn causes signal reflection. Therefore, the most commonly used linear topology is the hand-held connection. As shown in Figure 2, in order to ensure the reliability of communication, the node at the start end and the end need to add a 120Ω termination resistor, and it is not allowed to connect only one end or both ends. Figure 2 hand-held connection wiring diagram 2, T-branch connection In most industrial sites and rail locomotives, there are many wiring cables that need to be used for post-maintenance. Therefore, the node branch on the CAN bus is inevitable, and the branch length can only be minimized, as shown in Figure 3. Figure 3 T-branch structure The length of this branch is preferably within 0.3m at the highest baud rate of 1M. We can infer that if the branch length satisfies less than 0.3m under other baud rates, the bus communication can run stably. What can I do if I can't do such a short branch in some occasions? We can choose different branch lengths depending on the baud rate. As can be seen from Figure 4, as the baud rate increases, the branch constraints become more and more strict. On the contrary, if you want to increase the length of the branch, the baud rate must be reduced to obtain stable communication. Figure 4 Relationship between baud rate and branch length 3, star topology Figure 5 isometric star connection As shown in Figure 5, if you use the same length star topology for wiring, you can use the hub device without proper use. Adjust the termination resistance of each node to achieve networking. R=N&TImes; 60Ω N: number of branches R: terminating resistance of each branch Note that each node must have a terminating resistor and no resistors can be added to the center of the star network. In real-world applications, it is not possible to make an equal-length star connection in many cases. At this time, we need to use a CAN hub to branch, as shown in Figure 6. Figure 6 Hub for complex branch networks The use of hub cabling is very flexible and can be arbitrarily branched as needed, with fewer constraints. Electronic motors specilized for honeycomb blinds. Roller Blind Drive,Skylight Shade Motor,Honeycomb Blinds Motors,Roller Blind Motor GUANGDONG A-OK TECHNOLOGY GRAND DEVELOPMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.a-okmotor.com