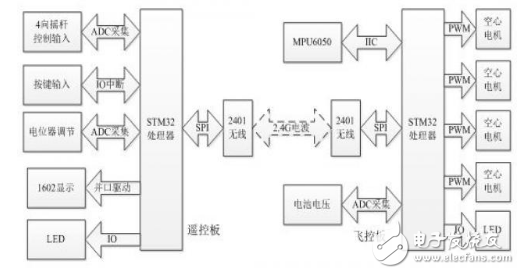
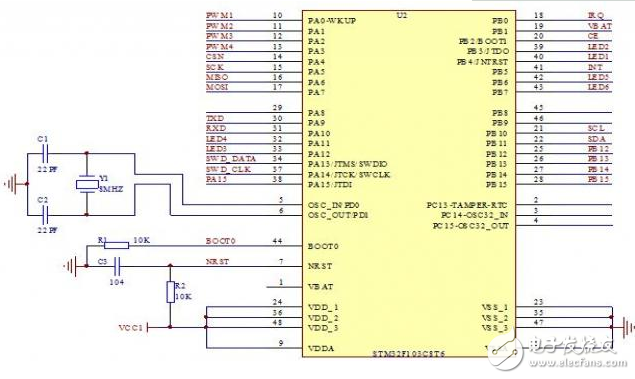
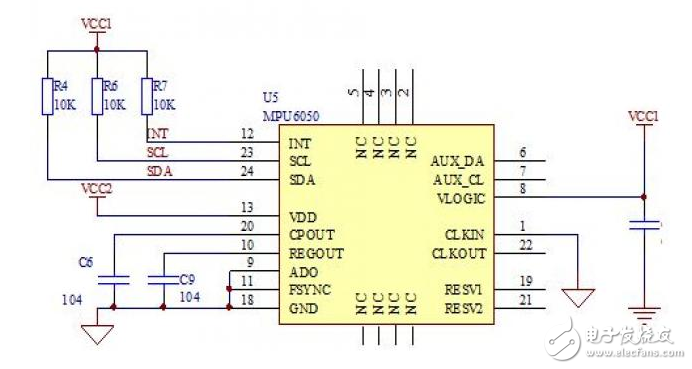
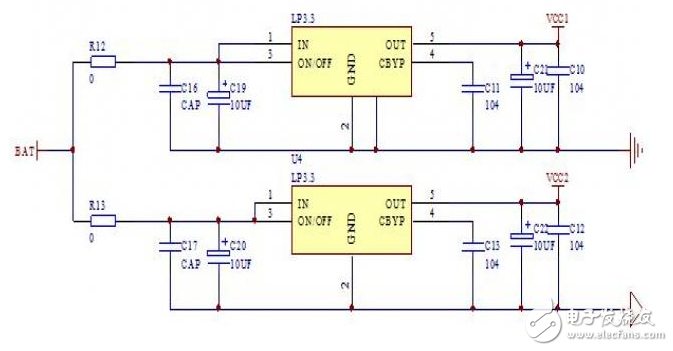
Introduction The quadcopter is a compact, unique type of vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft. Compared to traditional aircraft, it offers advantages such as a simple structure, lower failure rate, and higher lift per unit volume. It has found applications in both military and civilian fields, showing great potential for use in tight or confined spaces. As a result, the quadrotor has become a popular subject for research, attracting many engineers and becoming a growing area of interest globally. This project aims to develop a basic four-axis drone system using technologies such as Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) attitude sensing, PID motor control algorithms, 2.4G wireless remote communication, and high-speed hollow-cup DC motor drives. The system consists of two main parts: the flight control module and the remote control module. The flight control part integrates the frame and control core to enhance system stability, while the remote control uses an analog joystick for intuitive operation. Communication between the two modules is ensured via a 2.4G wireless module, providing reliable data transmission. The flight control board is powered by a high-speed STM32 microcontroller, with the MPU6050 sensor used for attitude measurement. Data is processed using a PID algorithm, and motor control is achieved through PWM signals to enable remote control of the drone's movement. The hardware design of the system includes two main components: the remote control board and the flight control board. The remote control board is designed to resemble a game controller, featuring a four-way joystick for input and a 2.4G wireless module for transmitting data. The flight control board uses an integrated design where the processor and motor drivers are combined on a single circuit board, making it compatible with standard toy-sized components. The software architecture also includes two parts: one for the remote control and one for the flight control. The remote control software handles ADC signal acquisition and wireless data transmission, while the flight control software processes incoming signals, calculates the drone’s orientation, and adjusts the motors using PID control. The final output is controlled via PWM to stabilize the drone’s flight. A block diagram of the entire system is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1: System Overall Design Block Diagram Considering cost and performance, the main control unit for both the flight and remote control boards is based on the STM32F103 from STMicroelectronics. This microcontroller is built on the ARM Cortex-M3 32-bit architecture, operating at up to 72MHz. It features 64K or 128K of flash memory, up to 20KB of SRAM, two 12-bit ADCs with 16 channels, a 7-channel DMA controller, up to 80 I/O ports, and multiple communication interfaces including I²C, SPI, USART, CAN, and USB. These features make it ideal for real-time control and sensor data processing. A schematic of the main control unit is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: Schematic of the Main Control Unit The key components of the flight control board include the MPU6050 inertial sensor, the NRF24L01 wireless module, and the motor drive circuit. The MPU6050 is connected via the I²C interface, with its SCL pin connected to PB10 and the SDA pin to PB11 of the STM32. An interrupt pin is connected to PB5 to trigger data updates. Pull-up resistors are added to each I²C pin to ensure stable signal transmission. A schematic of this setup is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3: Inertial Measurement Unit Schematic on Flight Control Board Power supply is another crucial part of the system. A 3.7V high-discharge-rate lithium battery is used to power the drone. The main control chip and the IMU sensor are supplied independently through low-dropout regulators (LDOs), ensuring stable voltage and accurate sensor readings. A schematic of the power regulation module is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4: Power Supply Voltage Regulator Schematic Ei 76 Transformer,76V Transformer,Ei-76 Transformer,Audio Output Transformer,low voltage lighting transformer Guang Er Zhong(Zhaoqing)Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.geztransformer.com