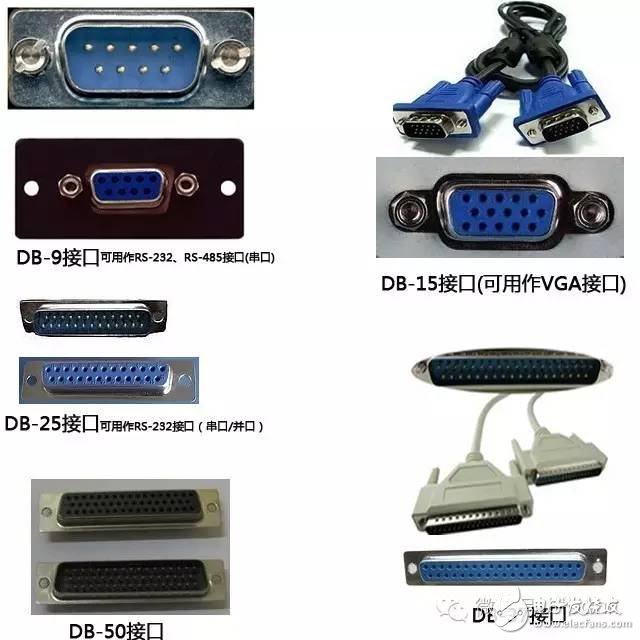
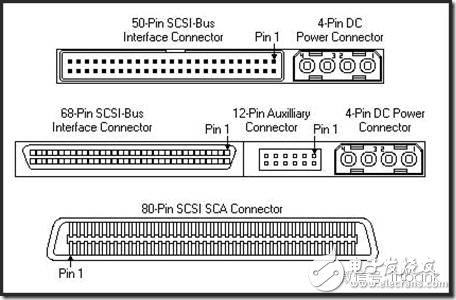
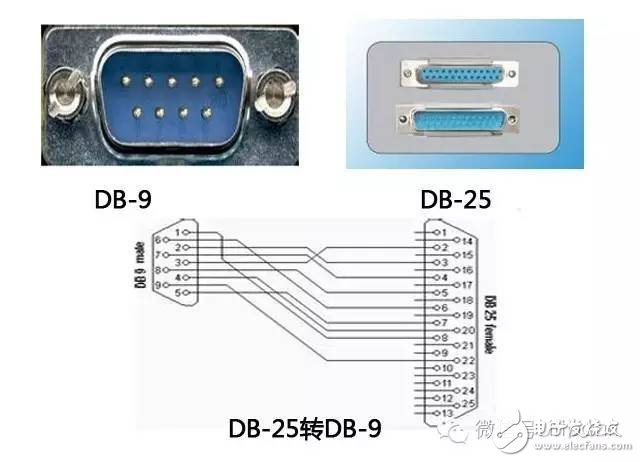
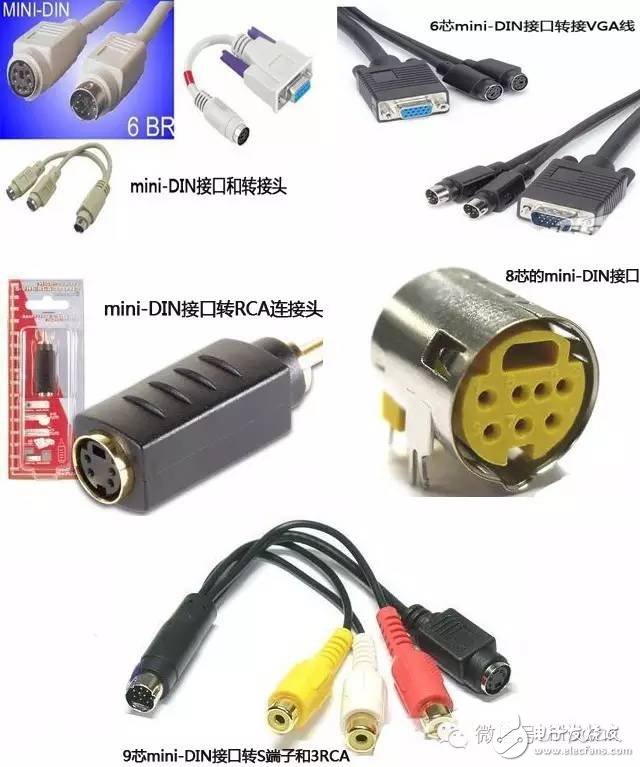
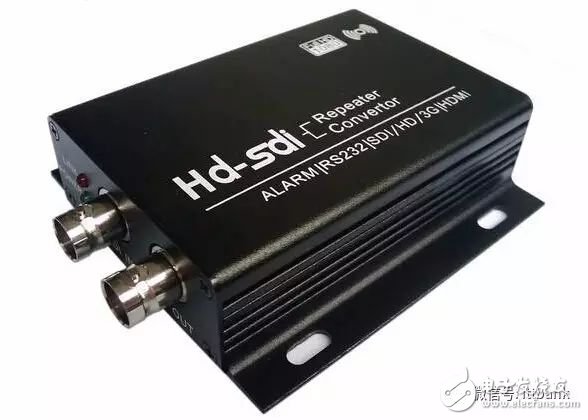
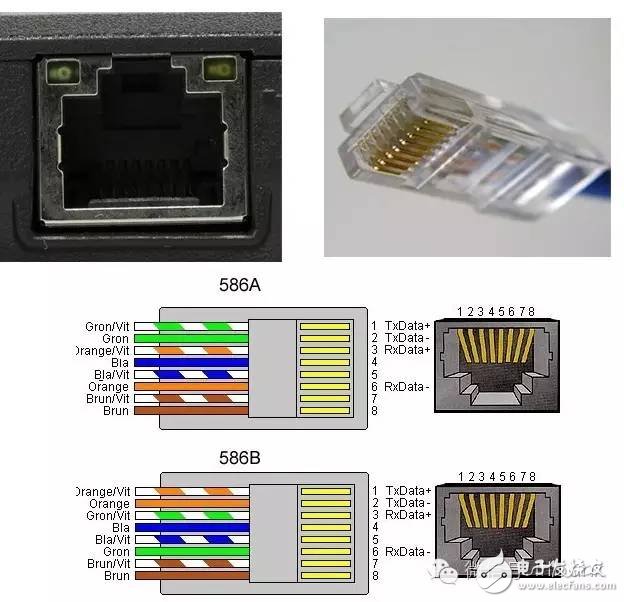
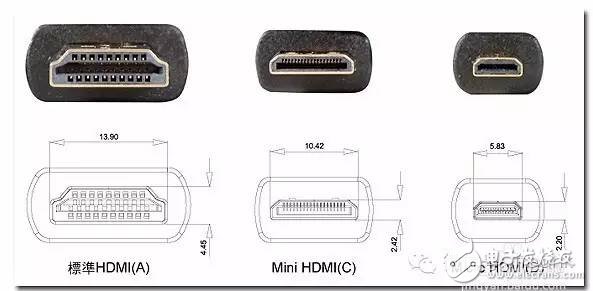
Electronic equipment comes with a variety of transmission interfaces, and new types of interfaces continue to emerge. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the names, physical appearances, and functions of these interfaces, aiming to help readers better understand them. The term IDE stands for "Integrated Drive Electronics," which refers to a hard drive that integrates the "hard disk controller" with the "disk." It was commonly used in consumer products but also found in some servers. The main advantages include low cost, strong compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, it has drawbacks such as slow data transfer speeds, short cable lengths, limited number of connected devices, and no hot swap support. Over time, various standards like ATA 66, ATA 100, and ATA 133 were developed to improve performance. Although IDE interfaces have been largely replaced by SATA, they played a crucial role in early computing history. IDE Interface Advantages: low price, strong compatibility, cost-effective Disadvantages of the IDE Interface: slow data transmission, short cable length, few connected devices, and no hot swap Development Path: Initially, the IDE interface had two transfer modes: PIO and DMA. While DMA was more efficient, it required additional drivers, making it less popular. As speed demands increased, manufacturers introduced faster standards like Ultra DMA 33, ATA 66, and eventually ATA 133. These standards were backward compatible, allowing older devices to work with newer ones. Despite its limitations, IDE laid the foundation for modern storage technologies and eventually gave way to SATA. In Summary: IDE represents an early type of hard disk interface, specifically the original ATA-1 standard. While it has been phased out due to technological advancements, it served as the basis for later developments like ATA, Ultra ATA, and Ultra DMA. Today, hardware has moved towards SATA, and the IDE interface is gradually becoming obsolete. SCSI stands for "Small Computer System Interface." Unlike IDE, which is standard for personal computers, SCSI is a high-speed data transmission technology primarily used in small computers. It's known for its wide application range, multi-tasking capabilities, large bandwidth, low CPU usage, fast speed, and hot-swapping support. However, SCSI interfaces are expensive, difficult to install, and require driver setup, which limits their use to medium and high-end servers and workstations. SCSI Interface Advantages: wide application range, multi-tasking, large bandwidth, low CPU usage, fast speed, high transmission rate, hot swap, etc. Disadvantages of SCSI Interface: high price, inconvenient installation, and need to set up and install drivers to prevent formatting confusion. SATA stands for "Serial ATA," a new type of hard disk interface that differs from Parallel ATA by using serial data transfer. It is the future trend for PC hard drives. Introduced in 2001, the SATA 1.0 specification defined a maximum data transfer rate of 150MB/s, surpassing the 133MB/s of parallel ATA. Subsequent versions like SATA 2.0 and 3.0 increased the speed to 300MB/s and 600MB/s, respectively. SATA offers benefits such as serial data transmission, one-to-one connection, hot plugging, reliable data transmission, and potential for bandwidth upgrades. However, older motherboards may not support SATA without additional drivers. The hard disk using SATA (Serial ATA) port is also called serial port hard disk, which is the trend of PC hard disk in the future. In 2001, the Serial ATA 1.0, which consists of Intel, APT, Dell, IBM, Seagate, and Maxtor, officially established the Serial ATA 1.0 specification. In 2002, although serial ATA related equipment have not yet been officially launched, the Serial ATA committee has preemptively established the Serial ATA 2.0 specification. Serial ATA adopts serial connection mode. Serial ATA bus uses embedded clock signal and has stronger error correction capability. Compared with the past, the biggest difference is that it can check the transmission command (not just data). The error is automatically corrected, which greatly improves the reliability of data transmission. Serial ATA 1.0 defines a data transfer rate of up to 150MB/s , which is higher than the fastest parallel ATA (ie ATA/133) with a maximum data transfer rate of 133MB/s, while the data rate in Serial ATA 2.0 is higher. At 300MB/s , the final SATA will achieve the highest data transfer rate of 600MB/s . There will be faster SATA Express specifications in the future. Advantages of SATA Interface: serial data transmission, one-to-one connection without the trouble of the master and slave disks, support for hot plugging, more reliable data transmission, low voltage signal, potential for bandwidth upgrade Disadvantages of SATA Interface: It is not too big for PC users. The old motherboard uses SATA interface. When installing the operating system, you need to use the floppy disk. The old motherboard does not support SATA hard disk. Fibre Channel is a high-speed data transmission technology originally designed for network systems. It has gradually been applied to hard disk systems as storage requirements increase. Known for multiple connected devices, low CPU usage, remote connectivity, high bandwidth, versatility, hot swapping, and fiber/copper connections, Fibre Channel is typically used in high-end servers due to its high cost and complex setup. Advantages of Fibre Channel: multiple connected devices, low CPU usage, remote connectivity, high bandwidth, versatility, hot swappable, fiber and copper connections, etc. Fibre Channel Shortcomings: expensive products and complex builds Infrared communication is a low-cost, short-range, non-connected, low-power, and confidential communication method. It is mainly used for wireless data transmission in PCs and has gradually expanded into wireless networks. It is also used in remote control appliances. Most motherboards now provide infrared interfaces, enabling users to communicate with devices that have infrared interfaces, such as laptops, printers, modems, handheld computers, and mobile phones. However, the infrared interface is only provided on the computer motherboard, and the complete transmitting and receiving device is not included. Therefore, users still need to purchase an infrared connector to use this feature. D-type data interface, an interface standard for connecting electronic devices (such as computers and peripherals). Because the shape is similar to the English letter D, it is named D-type interface. According to the number of interfaces, it is subdivided into type A (15-pin), B-type (25-pin), C-type (37-pin), D-type (50-pin), and E-type (9-pin). The common computer parallel port is the DB25 pin connector, and the serial port should be the DE9 pin connector. Since the serial port and parallel port of the early computer used DB25 pin connector, people used to put the letter B and D together and recorded it as the common name of the D-type interface, so that the computer serial port was changed to 9-pin. After the interface, people use DB9 instead of DE9 to call the 9-pin interface. The result of this further promotion is that people now use DBxx to represent the D-type interface, and the number xx is the number of pins on the interface. PCI stands for "Peripheral Component Interconnect," which is the most widely used interface in personal computers. It is available on almost all motherboard products. The PCI slot is also the motherboard with the largest number of slot types. On the current popular desktop boards, the ATX-based motherboards usually have 5 to 6 PCI slots, while the smaller MATX motherboards also have 2 to Three PCI slots show the wide range of applications. However, due to its limited bandwidth of 133MB/s, it is insufficient for powerful graphics cards, leading to its decline in use today. Since the PCI bus has only 133MB/s of bandwidth, it is more than enough for most input/output devices such as sound cards, network cards, and video cards, but it is unable to meet the needs of increasingly powerful graphics cards. At present, the graphics cards of the PCI interface are rare, and only on older PCs, and manufacturers rarely introduce such interfaces. PCI-Express is the latest bus and interface standard. Its original name is "3GIO", which was proposed by Intel. It is obvious that Intel means that it represents the next generation I/O interface standard. It was renamed "PCI-Express" after the release of PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Organization) certification, referred to as "PCI-E". The latest version is PCI-E 2.0. The PCI Express 2.0 specification has made a major upgrade in data transfer speed, which is doubled from the previous 2.5Gbps bus frequency to 5.0Gbps, which means that PCI Express 2.0 x16 The interface can be doubled to an amazing 10GB/s bus bandwidth (1GB/s = 8Gbps). Serial port (also known as serial port), also known as serial communication interface (usually referred to as COM interface), is an extended interface using serial communication. Common RS-232 for general computer applications (using 25-pin or 9-pin connectors) and half-duplex RS-485 and full-duplex RS-422 for industrial computer applications. RS-232 Interface One of the communication interfaces on personal computers, the asynchronous transmission standard interface developed by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA). Usually the RS-232 interface appears in the form of 9 pins (DB-9) or 25 pins (DB-25). Generally, there are two sets of RS-232 interfaces on the personal computer, which are called COM1 and COM2. . RS-232 is one of the mainstream serial communication interfaces. Due to the early appearance of the RS232 interface standard, it is inevitable that there are deficiencies, mainly the following four points: (1) The signal level of the interface is high, which is easy to damage the chip of the interface circuit. (2) Low transmission rate (3) weak anti-noise interference (4) The transmission distance is limited, and the maximum transmission distance is 50 feet. RS-422 Interface The full name of the standard is "the electrical characteristics of the balanced voltage digital interface circuit", which defines the characteristics of the interface circuit. A typical RS-422 is a four-wire interface. There is actually a signal ground, a total of 5 lines. Its DB9 connector pin definition. The RS-422 has a maximum transmission distance of 1219 meters and a maximum transmission rate of 10 Mb/s. The length of the balanced twisted pair is inversely proportional to the transmission rate, and it is possible to reach the maximum transmission distance below the 100 kb/s rate. The highest rate transmission is only possible at very short distances. The maximum transmission rate that can be obtained on a typical 100-meter twisted pair is only 1 Mb/s. RS-485 Interface It is based on RS-422, so many electrical regulations of RS-485 are similar to RS-422. The PS/2 interface is a 6-pin round interface with 2 pins that are idle. PS/2 is one of the most common interfaces on older computers for devices such as mice and keyboards. In general, the PS/2 interface mouse is green and the keyboard is purple. The PS/2 interface is the input device interface, not the transmission interface. Therefore, the PS2 port has no concept of transmission rate at all, only the scanning rate. Compared with the USB interface, the weakness of the PS/2 interface is: it does not support hot swapping. (If you enter the system, you think of the PS/2 keyboard or the mouse is not connected. If you can't use it, you must restart it. The keyboard and mouse are processed through the boot detection process; it is easy to bend or even break the pins of the PS/2 keyboard and mouse interface when connected. Before the PS/2 interface appeared, the mouse interface was a serial port (i.e., a COM serial interface, which is a 9-pin or 25-pin D-type interface, as described in point 5 above). This interface has the most applicable range and models. From the old computers without PS/2 and USB interfaces to the latest computers. Unfortunately, the serial port does not support hot swapping. It is said that the data transfer rate is also very slow. But this interface has not been eliminated so far, although it is rarely used by the average person. USB is the abbreviation of English UniversalSerialBUS. The Chinese meaning is "Universal Serial Bus", which is a technology developed for transferring data between PC and digital devices. Standard USB, Mini USB (typical application: MP3), Micro USB (typical application: Android smartphone) has become the most common USB interface. It is widely used in information communication products such as personal computers and mobile devices, and is extended to other related fields such as photographic equipment, digital television (set-top boxes), and game consoles. USB evolved from USB 1.0 to the latest USB 3.1. USB1.1 : Launched in September 1998, 12Mbps (1.5MB/s), Full-Speed, 500mA USB2.0 : Launched in April 2000, 480Mbps (60MB/s), High-Speed, 500mA USB3.0 : Launched in November 2008, 5Gbps (640MB/s), Super-Speed, 900mA USB 3.1 : The transmission speed is 10Gbit/s, the three-stage voltage is 5V/12V/20V, and the maximum power supply is 100W. The new Type-C plug-in is no longer positive and negative. As early as December 2013, the USB 3.0 promotion team announced the rendering of the next-generation USB Type-C connector, and then began mass production in August 2014. The highlights of the new interface are a slimmer design, faster transfer speeds (up to 10Gbps) and more powerful power transfer (up to 100W). The biggest feature of the Type-C double-sided pluggable interface is that it supports double-sided insertion of the USB interface, and formally solves the worldwide problem of "USB can never be inserted", and the front and back are plugged in casually. At the same time, the USB data cable used with it must also be thinner and lighter. Do Type-C PD chip manufacturers: Microchip, Cypress, NXP, ROHM, Technology Semiconductor, Power Integrations, etc. Appearance Characteristics Ultra-Thin: The thinner body needs a thinner port, which is one of the reasons why USB-C turned out. The USB-C port is 0.83 cm long and 0.26 cm wide. Old-fashioned USB ports are 1.4 cm long and 0.65 cm wide, which are outdated. This also means that the end of the USB-C data cable will be one-third the size of a standard USB-A data cable plug. Nothing is right and wrong: Like Apple's Lightning interface, the front and back sides of the USB-C port are the same. This means that no matter how you insert this port, it is correct. Users don't have to worry about the pros and cons of traditional USB ports. The Main Function Fast: In theory, the maximum transfer rate of the USB-C port is 10Gb per second. But Apple said the new MacBook's USB-C port has a maximum transfer rate of 5Gbps. The maximum output voltage is 20 volts to speed up charging time. The USB-A type has a limit transmission rate of 5 Gbps and an output voltage of 5 volts. All-Rounder : The new MacBook's USB-C port can transfer data, charge it, or link to an external display device as a video output port. The only question is how Apple meets users who want to do these three things at the same time. Two-Way: Unlike the old USB port, the power can only be transmitted in one direction. The power transmission of the USB-C type port is bidirectional, which means that it can have two transmission power modes. Therefore, users can now not only use a laptop to charge mobile devices, but also use other devices or mobile power to charge their laptops. Backward Compatibility: USB-C is compatible with older USB standards, but users need to purchase additional adapters to complete compatibility. Apple said that not only Apple will sell adapters, but third-party companies can also license production. The Dock interface is 9pin and 30pin. Apple started using the 30pin dedicated Dock interface from the iPod 10 years ago, and almost all data synchronization and peripherals rely on this interface. Since Apple launched the 9 Pin Lightning Dock interface on the iPhone 5 release, the release of the new interface standard also means that Apple's nine-year 30-pin Dock interface will be officially replaced. A typical VoIP phone will provide two RJ-11 interfaces. One RJ-11 interface is used to connect the telephone line connected to the HomePNA switch, and the other RJ-11 interface is connected to the telephone. The RJ45 interface is usually used for data transmission. The most common application is the network card interface. The TV interface is also called the RF input interface. The antenna and the analog closed-circuit TV are connected to the radio frequency (RF) interface. As the most common way to connect video, it can transmit both analog video and audio signals. The RF interface transmits the mixed video and audio signals, and the circuit of the display device combines the encoded signals for a series of separation and decoding at the output. Due to the need for video and audio mixing, the signals will interfere with each other, so its quality output quality is the worst of all interfaces. Cable connections are also commonly used in cable and satellite television receiving devices, but in this case they transmit digital signals. The earliest AV interface is the audio and video separation transmission interface, which consists of three colors of red, white and yellow. The yellow line is the video transmission line, and the red and white are responsible for the sound transmission of the left and right channels. The AV interface separates the video and audio to avoid interference between the audio and video. However, since the brightness and chrominance need to be decoded and displayed on the video transmission, the video transmission still has a loss, so the current high-definition video playback basically gives up the AV interface. The S terminal is also known as the mini-DIN interface in the name of some projector manufacturers. It consists of 4 cores (without audio output), 5 cores, 6 cores, 7 cores, 8 cores, 9 cores (6 sounds are available). Different signal products are used on the projector. The VGA terminal V on the notebook (other names include RGB terminals, D-sub 15, or mini D15) is a 3-row, 15-pin DE-15. The VGA terminal is usually on the computer's display card, display and other devices. It is used to transmit analog signals. Digital Video Interface, the digital video interface. A high-speed transmission digital signal technology invented by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG), established in September 1998 at the Intel Developer Forum, with DVI-A, DVI-D and DVI-I A variety of interface forms. DVI-D only has a digital interface, DVI-I has digital and analog interfaces, and the current application is mainly DVI-i (24+5). High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a digital video/audio interface technology. It is a dedicated digital interface suitable for image transmission. It can transmit audio and video signals at the same time. The maximum data transmission speed is 2.25 GB/s . HDMI has three interfaces. Mainly considering the needs of the equipment. If the size of a digital camera is small and a small interface is required, use micro HDMI. The three interfaces are only different in size and have the same function. The IEEE1394 interface is a serial standard developed by Apple, and the Chinese translation is called Firewire. Like USB, IEEE1394 also supports peripheral hot swap, which can provide power for peripherals, eliminating the power supply of peripherals, connecting multiple different devices, and supporting synchronous data transmission. IEEE1394 is divided into two transmission modes: Backplane mode and Cable mode. The minimum rate of Backplane mode is also higher than the maximum speed of USB 1.1, which is 12.5 Mbps, 25 Mbps, and 50 Mbps, respectively, and can be used in most high-bandwidth applications. Cable mode is a very fast mode, divided into 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps and 400 Mbps, which can transmit uncompressed high quality data movies at 200 Mbps. The IEEE1394 interface is available in 6-pin and 4-pin versions, which are commonly referred to as large and small ports. The 6-point connector is 6-pin and the small quad-angle connector is 4-pin. The IEEE1394 interface developed by Apple was 6-pin. Later, SONY took a fancy to its fast data transfer rate. It improved the early 6-pin interface and redesigned it into a 4-pin interface that is common nowadays. For iLINK. This type of connector requires a converter if it is to be connected to a standard 6-conductor cable. IEEE-1394 Interface Advantages: high speed, real-time, ease of use, bus structure, hot swap, plug and play. BNC, the full name is Bayonet Nut Connector (the name of the connector is described in the name), also known as the British Naval Connector (the British Navy connector, probably the first use of this connector by the British Navy) or Bayonet Neill Conselman (Neill Conselman bayonet, this joint was invented by a man named Neill Conselman). The BNC (Basic Network Card) interface is a 10Base2 connector shaft thin cable, that is, a coaxial thin cable connector for connecting analog signals. It is now mostly used for security industry monitors to transmit video signals and cable TV indoor wall interfaces. This interface is only available in some new products in displays larger than 17 inches. The BNC method has always been one of the features of professional-grade displays. However, BNC has recently been replaced by DVI digital video. Of course, BNC will continue to exist for a while before the price and sales volume of DVI equipment can't fully meet market needs. The color difference interface is based on the S interface, and the blue difference (b) and the red difference (r) in the chrominance (C) signal are separately transmitted, and the resolution can reach 600 lines or more. It usually uses two symbols, YPbPr and YCbCr, the former represents the progressive scan color difference output, and the latter represents the interlaced color difference output. Nowadays, many TV products rely on the color difference input to improve the input signal quality, and through the color difference interface, you can input multiple levels of signals, from the most basic 480i to the 480p of the multi-frequency scanning, even 720p, 1080i, etc. To pass the color difference input, there is a way to transmit the signal to the TV. The transmission distance of 75-2RGB is 30-50M, and the transmission distance of 75-3RGB is 50-70M. SDI (Serial Digital Interface) is a "Digital Component Serial Interface". Then HD-SDI is a high-definition digital component serial interface. HD-SDI is a real-time uncompressed high-definition radio and television-grade camera. It is another technological advancement in the field of security monitoring, providing high-definition image source equipment for the monitoring center. Audio Port: The RCA connector is often referred to as the Lotus Head. The use of RCA cables to transmit analog signals is currently the most common audio connection. Each RCA cable is responsible for transmitting the audio signal of one channel, so stereo signals require a pair of cables. For multi-channel systems, the same number of cables are used depending on the actual number of channels. Stereo RCA audio interface, generally the right channel is marked in red, and the left channel is marked in blue or white. The full name of S/PDIF is Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format , a civilian digital audio interface protocol developed by Sony and Philips. Due to its widespread adoption, it has become the de facto standard for civil digital audio formats. A large number of consumer audio digital products such as civilian CD players, DAT, MD, and computer sound card digital ports support S/PDIF
Yuchai High Voltage Generators with Yuchai Diesel Engine, HV AC Generator
·Engine and alternator shall be mounted on a same frame steel skid.
·Comply with ISO8528 national standard and ISO9001 quality standard.
. Voltage: 3kV, 3.3kV, 6kV, 6.3kV, 6.6kV, 10kV, 10.5kV, 11kV,13.8kV
Yuchai Hv Genset,Yuchai Hv Generator,Yuchai 10Kv Generator,Yuchai High Voltage Generator Guangdong Superwatt Power Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.swtgenset.com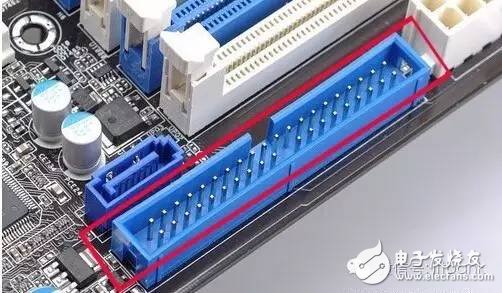








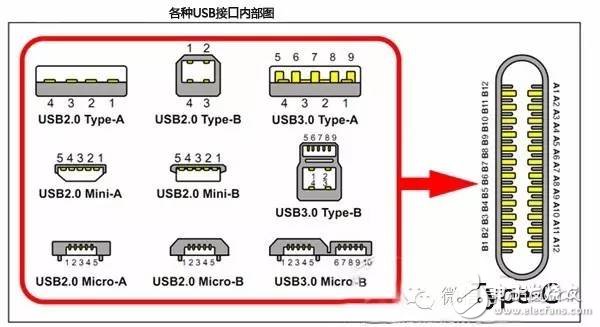 USB1.0 : Launched in January 1996, 1.5Mbps (192KB/s), Low-Speed, 500mA
USB1.0 : Launched in January 1996, 1.5Mbps (192KB/s), Low-Speed, 500mA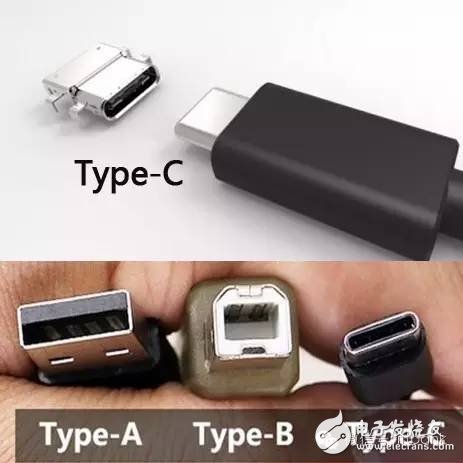 











·World most famous brand diesel engine: Yuchai engine
·World famous brand High Voltage AC alternator: Stamford, Leroy Somer, Marathon, Faraday, etc
·Advanced and reliable controller: Auto start, AMF & Remote control by PC with RS232/485
·Full range protect function and alarm shutdown feature.