Our company is specialized in supplying flaring tools. We have different kind of flaring tools including 45°ratchet eccentric cone type Flaring Tool,45°eccentric cone type flaring tools,electric cordless flaring tool,grabber flaring tool,etc.These precision tools provide smooth,uniform flares with minimum effort. It applies to wide range of applications, like installation and maintenance of household air conditioner,automobile air conditioner,refrigerator,cold room and other industries which need to be flared. Flaring Tool Flaring Tool,Pipe Flaring Tool,Double Flare Tool,Brake Pipe Flaring Tool ZHEJIANG ICE LOONG ENVIRONMENTAL SCI-TECH CO.,LTD. , https://www.ice-loong.com
In recent years, the IEEE802.16 series of broadband wireless access technology standards have received widespread attention in the industry. Intel and other large-scale telecommunications equipment manufacturers have established the WiMAX Forum to coordinate the interoperability of network equipment and promote the development and popularization of WiMAX. As a broadband wireless access technology WiMAX positioned for outdoor applications, it has a series of remarkable features both from a technical perspective and an application perspective. Therefore, it has great appeal for both users and telecom operators.
However, the IEEE 802.16 series of standards only define the air wireless interface, which provides flexibility for upper-layer applications. At the same time, as a wireless metropolitan area network technology that solves the "last mile" problem, how to compete with the currently widely used cable method in the future metro network access application and give full play to the strengths of the wireless mode is also worth studying. The problem. Therefore, in this sense, it is of great value to determine its competitive application model. Here, first, the technology and application characteristics of WiMAX broadband wireless access are analyzed, and based on this, a preliminary discussion is made on its application mode.
2. Characteristics of WiMAX broadband wireless access
As a wireless access method for outdoor applications, WiMAX not only has the characteristics of general wireless access, but also has some other characteristics in terms of technology.
1. Application characteristics
First of all, WiMAX as a broadband wireless access application has the characteristics of gradual investment and flexible deployment. Network operators can gradually increase investment and gradually expand capacity in place according to the needs of user capacity growth to achieve a basically flat cost curve. Secondly, the network planning can be free from the restrictions of terrain and landforms, and the ministries are flexible. At the same time, areas with low user density can still achieve coverage at a lower cost, reducing the risk of initial investment. Thirdly, the network deployment is fast, installation and capacity expansion is convenient, no complicated network planning is required, and the network structure is flexible, especially in temporary and sudden emergency communications, which can play a huge role. Finally, as a broadband wireless access technology with a cell radius of up to 50km and an access rate of up to 70Mbit / s, it can be used as both a wireless extension of the metropolitan area network and an alternative to cable. In particular, it is more competitive than cable in areas where user density or traffic is not high and the distribution is scattered.
2. Physical layer characteristics
The WiMAX working frequency band can be from 2-66GHz (for IEEE802.16 standard: 2-11GHz; for IEEE802.16a standard: 10-66GHz), the channel bandwidth can be flexibly adjusted in the range of 1.5-20MHz, which is beneficial to the allocated channel bandwidth Make full use of the spectrum resources within.
WiMAX adopts macro cell mode with a maximum coverage of 50km. When the channel bandwidth is 20MHz, it supports a shared data transmission rate of up to 70Mbit / s (in this case, the maximum coverage is 3-5km). Multi-sector technology can be used to increase system capacity. One sector can simultaneously support more than 60 enterprise users using E1 / T1 or hundreds of home users.
WiMAX uses OFDM, receive / transmit diversity, adaptive modulation and other advanced technologies to achieve non-line-of-sight NLOS and blocked line-of-sight ONLOS transmission, which effectively improves the efficiency of wireless transmission in the city.
The physical layer supports two wireless duplex multiple access modes, TDD / DMTA and FDD / TDMA, to meet the requirements of telecommunication systems in different countries or regions. It supports three modulation modes: single carrier (SC), OFDM (256 points), OFDMA (2048 points), and can be flexibly selected according to needs. The physical layer can dynamically adjust the modulation method and physical layer parameters (for example: modulation parameters, FEC parameters, power levels, polarization methods, etc.) according to changes in transmission channel performance to ensure better transmission quality.
3. MAC layer features
Support QoS management to meet the requirements of different service quality. The MAC layer requests connection bandwidth or performs bandwidth adjustment in a polling manner according to service QoS requirements and service parameters to ensure low latency requirements for real-time services such as voice and video. At the same time, for the high bit error rate and packet loss rate in the wireless channel environment, ARQ based on each application stream is defined to ensure the automatic retransmission of the MAC layer service data unit MSDU to ensure the end-to-end packet transmission quality.
The MAC layer has an ATM service and packet service convergence sub-layer CS, which can easily implement network applications featuring ATM services or IP services. At the same time, the MAC layer has a security sublayer that supports the MAC layer security mechanism to implement security management such as authentication and encryption.
4. Business Capability
WiMAX uses a connection-oriented approach to provide users with data, video and voice (VoIP) services with QoS performance. In the IEEE802.16 standard, the MAC layer defines a relatively complete QoS mechanism, and also defines four different services, namely: unsolicited bandwidth allocation service (UGS), real-time polling service (rtPS), non-real-time round Inquiry service (nrtPS) and best effort service (BE) can be used to provide users with high-quality video and voice services, ordinary-quality video and voice services, and services such as the Internet without quality assurance. Can dynamically allocate bandwidth according to the actual needs of the business, with greater flexibility. Therefore, WiMAX can provide different QoS for different services.
5. Network structure characteristics
Supported point-to-multipoint (PMP, PointtoMulTIpoint) architecture can build a star access network structure centered on WiMAX base stations. The newly released IEEE802.16a also supports mesh mesh architecture, which allows multiple WiMAX nodes to construct a mesh network using wireless interconnection. This means that the structure of the access network can be flexibly expanded, and WiMAX mesh network coverage can be used in areas where the backbone network cannot reach it, so as to achieve the flexible extension of the metropolitan area network.
3. WiMAX Broadband Wireless Access Application Mode
The technical characteristics and application characteristics of WiMAX determine that it can adapt to various application environments and have different application modes. The following is a preliminary analysis and discussion of the application mode of WiMAX broadband wireless access.
1. PMP application mode
As shown in Figure 1, the PMP application mode uses a base station (BS) as the core and uses a point-to-multipoint connection to build a star-shaped WiMAX access network. The base station (BS) plays the role of a service access point (SAP, ServiceAccessPoint). Through dynamic bandwidth allocation technology, the base station (BS) can flexibly select directional antennas, omnidirectional antennas and multi-sector technologies according to the situation of users in the coverage area. The user station (SS, Subscriber Station) equipment needs to access the core network. When necessary, the wireless coverage can be expanded through relay stations (RS, RepeatStaTIon). It can also flexibly divide the channel bandwidth according to the change in the number of user groups, expand the network, and realize the coordination of benefits and costs. 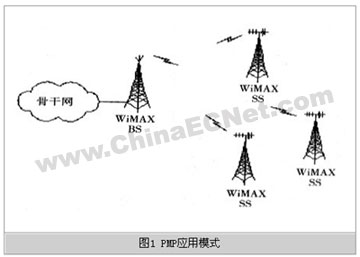
PMP application mode is a commonly used access network application form, which is characterized by a simple network structure, the application mode is similar to xDSL and other cable access forms, so it is an ideal choice for cable replacement.
2. Mesh application mode
As shown in Figure 2, the Mesh application mode uses multiple base stations (BS) to expand the wireless coverage area in a mesh network. Among them, there is a base station as a service access point (SAP) connected to the core network, and the remaining base stations (BS) are connected to the SAP with a wireless link. Therefore, the base station as SAP is both an access point for services and a convergence point for access, while the remaining base stations are not simple relay station (RS) functions, but access points for services. 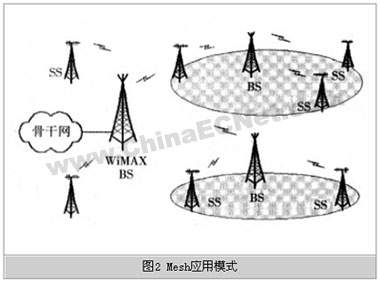
The characteristic of Mesh application mode lies in the mesh network structure, which can be deployed flexibly according to the actual situation and realize the flexible extension of the network. For areas such as suburban areas that are far from the backbone network and are not easily covered by cable, this mode can be used to expand the coverage. The specifications depend on factors such as the radius of the base station and the size of the coverage area.
3. Hotspot backhaul mode
As shown in Figure 3, the hotspot backhaul mode uses a WiMAX wireless access network to send remote WiFi hotspot Hotspot services to the core network. The WiMAX base station (BS) still functions as a service access point (SAP), while WiMAX The subscriber station (SS) is a wireless access device on the hotspot side. It provides a standard interface to connect to the hotspot. As a WLAN access point (AP, AccessPoint), the hotspot device is connected to the wireless terminal through the IEEE802.11a / b / g wireless link . 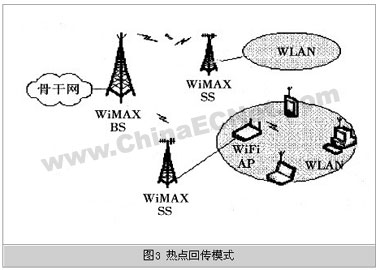
WiMAX access network can flexibly adopt PMP or Mesh structure according to the actual situation. For mobile operators, this application mode can also be used to transmit the mobile base station services of each cell back to the mobile switching center.
The main feature of the WiMAX hotspot backhaul mode is that it is used as a service backhaul application and uses wireless transmission. Compared with the traditional wired backhaul mode, its characteristics are obvious, and it can be used as a supplement or alternative to the traditional backhaul mode.
4. Terminal access mode
As shown in FIG. 4, in the terminal access mode, user terminal equipment (TE, Terminal Equipment) directly accesses the core network through a WiMAX base station (BS) as SAP. If the user terminal equipment (TE) wants to directly access the WiMAX network, it must be equipped with a subscriber unit (SU, Subscriber Unit) that conforms to the WiMAX standard. The subscriber unit (SU) is generally in the form of a WiMAX wireless network card or wireless module. 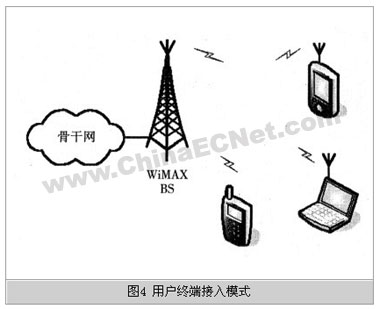
Because the WiMAX access rate is very high, and supports the mobility of terminal devices in the metro area (for the upcoming IEEE 802.16e), it is particularly suitable for terminal applications with high access rate requirements and mobility requirements.
The feature of this mode is that it allows user terminals to directly access the network at high speed, and supports the movement and roaming of portable terminals within the metropolitan area. From the perspective of technology and business, as long as the function of supporting VoIP voice service is added, it can become a veritable next-generation mobile communication network.
5. Resident network access mode
As shown in Figure 5, the access mode of the resident network is mainly aimed at group users, and its goal is to connect the resident network of users such as enterprises, campuses, and SOHO (Smalloffice Home Office) to the metropolitan area network through WiMAX. Same as other application modes, the base station (BS) is also connected to the core network as SAP to provide wireless access services. On the user side, the user wireless access device SS is connected to the base station (BS) through a wireless interface on one side and connected to the CPN device on the customer premises network through a standard interface (such as an Ethernet interface, E1, etc.). General user stations (SS) use directional antennas and various adaptive technologies to flexibly adjust the working mode to ensure the normal access of users. 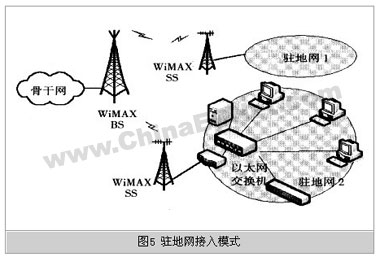
The CPN equipment on the customer premises network can be user routers, switches, hubs and other network equipment, or even another wireless access point (such as a WiFi hotspot), which is used to form a user-specific local area network. Network, enterprise network, government network or SOHO.
The access mode of the resident network is particularly suitable for inter-residential access applications where the cable access is inconvenient and the access bandwidth requirements are not high. Compared with the cable access method, fast deployment is the competitive advantage of this model.
6. Wireless bridge mode
As shown in Figure 6, the wireless bridge mode is a point-to-point wireless link, similar to the role of a remote network bridge. Its purpose is to connect two sub-networks with geographically separated locations together via a WiMAX wireless link. Because the wireless bridging uses a point-to-point method, the directions of the WiMAX wireless bridge device antennas at both ends can be aligned and fixed to each other, so the transmission performance is relatively stable and the deployment is relatively simple. 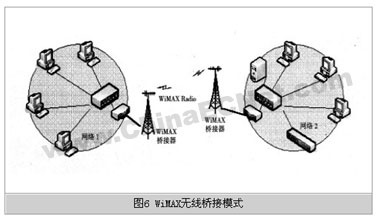
Obviously, the use of WiMAX wireless bridging can avoid difficult special line laying or pay expensive cable rentals, and can be quickly opened for use. The connection distance is long, and the connection bandwidth can fully meet the needs of general applications. In terms of user private network construction, it is more competitive than cable bridging.
4. Conclusion
From the perspective of network structure and application, WiMAX wireless access technology has all the advantages brought by wireless technology. At the same time, from a technical point of view, efficient modulation technology improves spectrum utilization; QoS mechanism improves business capabilities; macro cell coverage, especially It is suitable for outdoor applications; and it overcomes the bandwidth bottleneck of wireless technology at a higher access rate and becomes a supplement or alternative way for cable transmission in the future. It is foreseeable that with the popularity of WiMAX technology and the reduction in equipment costs, it may become a very competitive means to solve the "last mile" of the information highway. The WiMAX application mode discussed in this article combines the network application environment with the characteristics of WiMAX, which can not only meet the needs of network applications, but also give full play to the performance advantages of WiMAX. Therefore, the determination of the WiMAX application mode has practical significance for its future application and development.
Characteristics and application mode of WiMAX broadband wireless access
I. Introduction