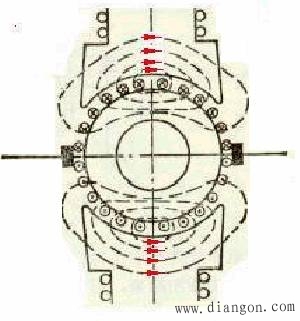
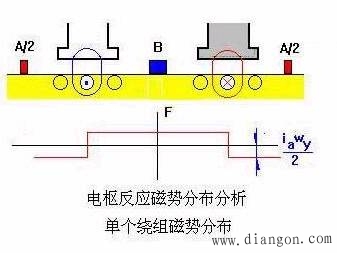
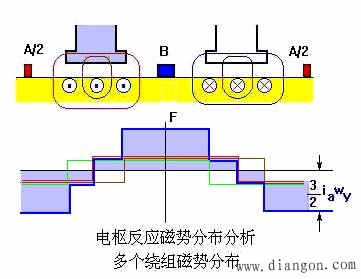
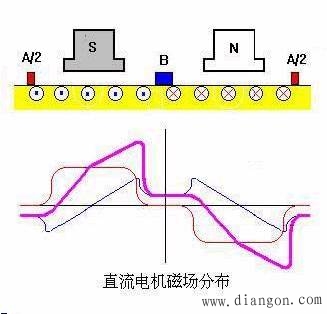
1. When a magnetic field motor is under load, current flows through the armature winding, creating a magnetomotive force. This flux is known as the armature magnetomotive force. As a result, the air gap magnetic field in the motor is formed by both the excitation magnetomotive force and the armature magnetomotive force. It's clear that in a DC motor, the air gap magnetic field changes from no load to load conditions. 2. Armature Reaction 1) The influence of the armature magnetomotive force on the air gap magnetic field produced by the field magnetomotive force is referred to as armature reaction. For simplicity in illustration, only one layer is shown on the edge of the element, and the armature is considered smooth. Considering the same direction of current flow in the component under a certain polarity, the distribution of the armature magnetic field can be determined. Figure 1.3..10 illustrates the air gap magnetic field distribution after the armature reaction. As seen, the position of the armature reaction flux potential axis always aligns with the brush axis. When the brush is placed at the geometric neutral line, the armature reaction magnetic potential is perpendicular to the magnetic pole axes. 5) The armature reaction distorts the air gap magnetic field. The armature magnetic field weakens the main magnetic field by half, while the other half strengthens it, resulting in zero magnetic density at the geometric neutral line. 6) Electromagnetic reaction leads to demagnetization. * When the magnetic circuit is not saturated, the weakening of the main magnetic field is exactly balanced by the strengthening effect. * When the magnetic circuit is critically saturated, the magnetization increases the saturation on one half of the pole, while reducing it on the other, leading to a slight decrease in the overall magnetic flux compared to the original. * Conclusion: Another consequence of the armature reaction is a reduction in the per-pole flux under motor load conditions. This effect has significant implications for motor performance and efficiency, especially under varying load scenarios. Wuxi Ark Technology Electronic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.arkledcn.com